I. What is an Exit Scam
An exit scam is a type of fraud that involves an individual, organization, or business building a reputation for their project in order to attract investors, and then disappearing with the collected funds

II. How to Exit Scam Operate
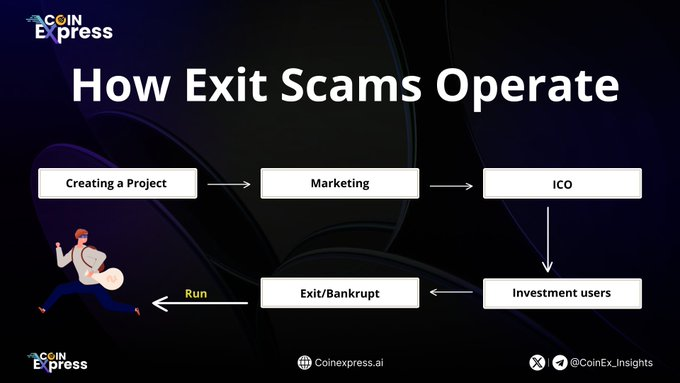
2.1 Creating a Project: Exit scam projects are often created in a hasty and unprofessional manner.
2.2 Maketing: Scammers create and heavily market a project, often with lofty promises of high returns to draw in investors.
2.3 ICO: Opportunities are opened for investment, frequently through unconventional and unregulated methods like ICOs or direct fundraising.
2.4 Investment users: Users who have invested cryptocurrency in this scam project
2.5 Exit/Bankrupt: Scammers disappear with the invested funds, taking down the project website, social media presence, and any other way investors can reach them. This is the core action in an exit scam and the primary concern forn investors
2.6 Run: After raising significant capital, the perpetrators vanish with the money, leaving investors with valueless assets
“It’s important to note that executing an exit scam doesn’t always require deep technical knowledge. The simplicity of the scam can make it dangerously effective”
III. Common Types of Exit Scams

3.1 ICO: A notorious method in the crypto market, where projects raise funds through ICOs and then abruptly shut down.
3.2 CEX Exit Scam: Centralized exchanges suddenly close or disappear, taking user assets with them.
3.3 Rug Pull: Developers withdraw liquidity from a project, plummeting asset values.
3.4 NFT Rug Pull: Similar to rug pulls, but specifically in the NFT space, where project creators abandon the project and devalue the NFTs
IV. How to Recognize an Exit Scam
4.1 Promises of High Returns: Unrealistic profit promises are a major red flag.
4.2 Simplistic Whitepaper: A lack of detail or clarity in the project’s whitepaper is a warning sign.
4.3 Continuous advertising of Token Price: An emphasis on rapidly increasing token prices over actual utility.
4.4 Lack of Security Audits: The absence of thorough security checks on the project’s technology.
4.5 Absence of Project Team Infomation: Anonymous or unverifiable team members are a cause for concern.
4.6 Ponzi Scheme Operations: Systems where returns for older investors are paid with the capital from new investors.
“By understanding these signs and staying informed, investors can better protect themselves from becoming victims of exit scams. Remember, if something sounds too good to be true, it often is. Always conduct thorough research before investing in any project.” References: Coin98 Insight, Investopedia














